Every field around the world has its own special jargon and a particular vocabulary that keeps evolving over time. The same holds true for project management. Over the years, just like the discipline itself, the lingo has also developed unique project management terms that one should know.
Compiled below are some of the most commonly referred to project management concepts and key terms that’ll benefit you even if you’re a seasoned pro. Go ahead and give your vocabulary the boost it deserves.
General Project Management Terms
1. Project Plan
A project plan is one of the key formal documents created before starting any project. The document usually consists of approved cost, schedule, and project scope. It guides the execution of a project from initiation to project closure. The project plan also lays the foundation for all kinds of communication among the stakeholders.
Find the best project planning tools here:
The 19 Best Project Planning Tools of 2024
2. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A work breakdown structure comprehensively divides the project deliverables into manageable sections. This hierarchical organizing of the team’s work helps everyone understand the nature of work better and execute project goals effectively.
3. Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM is an algorithm particularly used for scheduling project activities. It is used to determine the step-by-step sequence of activities, which in turn determines the total time of the project. These activities must be completed according to this set sequence to achieve the project goals.
4. Project Manager
The person responsible for handling every aspect of a project from the day it starts till it closes is called a project manager. The responsibilities of a project manager typically entail powerful planning, smart resource utilization, and managing the scope of the project.
5. Project Stakeholder
Any individual who has a direct or indirect interest in a project is known as a project stakeholder. They usually affect or are affected by the project decisions being taken over the course of the project lifecycle. A stakeholder can be anyone from the project team, executives, sponsors, customers, or the end-users.
6. Project Portfolio Management
Project portfolio management (PPM) involves collective management of a series of projects to achieve organizational goals. It allows the teams to visualize the big picture of all projects and maximize the return on investment.
7. Collaboration
The process of actively involving each team member in project activities is called collaboration. The whole concept demands the development of an interconnected network through which individuals exchange information and monitor the project performance.
8. Agile Project Management
Agile project management is an iterative and incremental approach to delivering projects. The approach focuses on breaking down the project into small cycles, known as ‘iterations.’ These iterations are then prioritized in terms of urgency or importance. There are multiple frameworks associated with agile implementation, Scrum being one of the most popular ones.
9. Waterfall Model
Waterfall model is a traditional project management approach to the project lifecycle. The model works in a similar pattern to a ‘waterfall’. The project development takes place systematically, from one phase to another in a downward fashion. Each phase has to be completed before moving on to the next phase and there is no overlapping of the phases, making it difficult to make any amendments.
10. Project Budget
Project budget is a formally approved document featuring a comprehensive list of financial resources, including project expenses, required to complete a project.
11. Project Timeline
A project timeline outlines the project events in order of their occurrence. It captures exactly what needs to be done over the course of the project lifecycle and how it will be done.
Gantt Project Management Terms
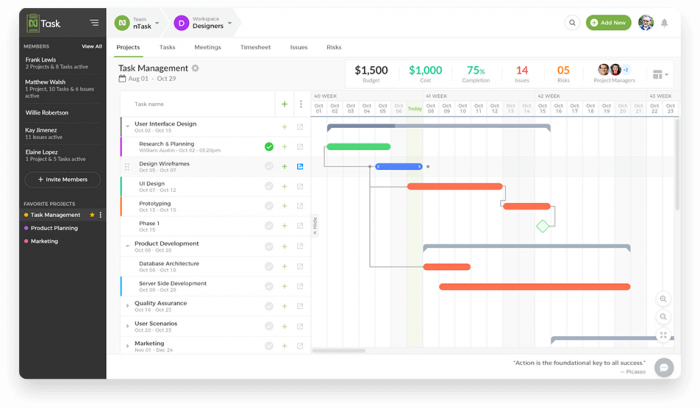
Simply put, Gantt charts are used for visualizing the project schedule in the form of a graph. The chart illustrates what needs to be done at a particular time period during the project lifecycle. The key terms associated with Gantt charts are:
12. Milestone
A milestone represents a major event in a project lifecycle. It is used as a reference point to measure the progress of a project. Usually represented as diamonds, milestones greatly help with project scheduling and monitoring.
13. Dependencies
Dependencies specify the relationship between project activities and the order in which they are to be performed. There are 4 kinds of dependencies:
- Start-to-start – The predecessor task must start before the Successor can start
- Finish-to-start – Predecessor must finish before the Successor can start
- Start-to-finish – The predecessor must start before the Successor can finish
- Finish-to-finish – The predecessor must finish before the Successor can finish
Kanban Project Management Terms
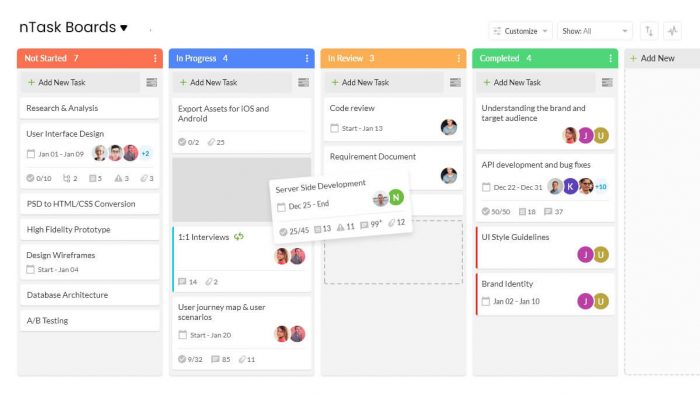
A popular project management methodology, Kanban uses a virtual pinboard approach to delivering projects. Utilizing movable cards to show the project’s progress overtime is essentially what makes up a Kanban system. When discussing Kanban, some of the commonly used project management terms are:
14. Work in Progress (WIP)
At any point during a project, the number of task items a team is currently working on is called work in progress. It indicates the capacity of the team’s workflow at any moment.
15. Work in Progress Limit
WIP limit restricts the maximum amount of work that can exist in different stages of a workflow. Limiting work in progress allows teams to identify bottlenecks faster and focus on single work items better.
16. Bottleneck
A bottleneck is a work stage where the inflow of workload is greater than the capacity of the system, resulting in hindering the smooth flow of work overtime.
17. Scrum
Scrum is a popular framework utilized for successfully implementing agile. The framework uses the iterative method of delivering projects and is based upon continuous systematic collaboration among team members in between the project cycle.
18. Sprint
A sprint is a fixed unit of time during which specific tasks has to be completed. Typically, the duration of a sprint is determined by the Scrum Master (team’s facilitator). During a sprint, daily standups are conducted to monitor the progress towards sprint goals.
Meeting Project Management Terms
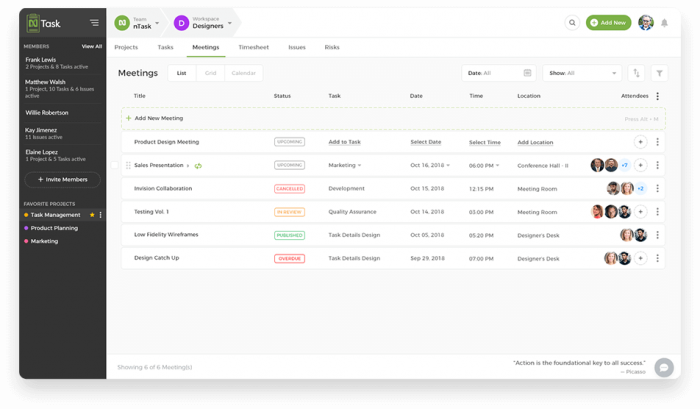
Professional team meetings are a core component of any project, but there are many meeting terminologies that a lot of us don’t know about. Some of these commonly used project management terms are:
19. Kickoff Meeting
A kickoff meeting is generally the first meeting that occurs between the project team and their client. This meeting usually occurs after the basic project details have been finalized, but the main project work has not been started yet. It serves the purpose of reviewing the project expectations and to create alignment between everyone involved in the project.
20. Meeting Agenda
A meeting agenda is simply a list of all the topics that are to be discussed during a meeting. It may include detailed topic descriptions, their sequence, and the expected outcomes of each topic.
21. Meeting Minutes
Meeting minutes are written notes of whatever is discussed during a meeting. These minutes can be circulated among meeting participants after the meeting to gain valuable insights and take appropriate follow-up actions.
22. Stand-up Meeting
A stand-up meeting, also known as the daily Scrum, is a daily short meeting conducted to get an update from every team member about their work progress. Usually, a stand-up meeting is conducted at the same time and same place every day.
23. Follow Up
A meeting follow-up includes all the activities that are targeted towards collecting feedback from the meeting participants after a meeting. Sometimes a dedicated follow-up meeting is conducted to serve the purpose.
Resourcing Project Management Terms
One of the most important project management concepts revolves around the term ‘resource’. Out of numerous terminologies associated with resource management, some are:
24. Resource Allocation
Resource allocation involves scheduling and assigning resources for a project in the most efficient way possible. The purpose of resource allocation is to maximize the use of available resources in a way that supports the project’s end goals.
25. Resource Breakdown Structure
A comprehensive list of resources required to complete a project. This list is usually made according to the function and resource type, facilitating the planning and control of a project work.
26. Resource Leveling
Resource leveling is the process of adjusting the project schedule in a way that keeps a resource use below a set limit. It ensures that a resource doesn’t have to work overtime. Resource leveling has an impact on the project’s critical path.
27. Resource Availability
Resource availability specifies whether a particular resource is available at a given time or not.
28. Resource Calendar
A resource calendar indicates all the working and non-working days a specific resource will be available.
Project Risk Management Terms
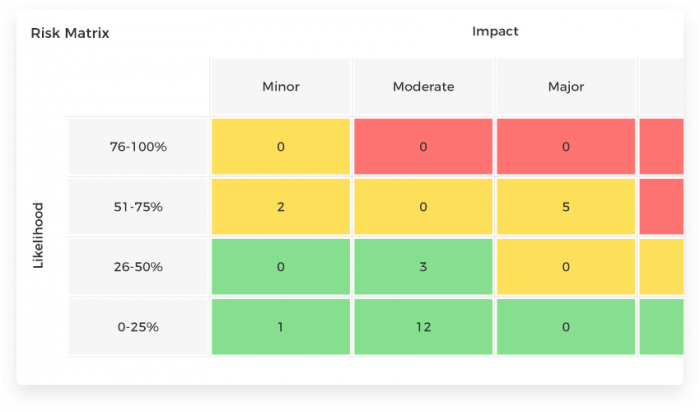
Any uncertain event or condition that has a probability of occurrence during a project is typically known as a project risk. Risks usually have the potential to impact the overall project objectives. Some common project management terms related to project risk tracking include:
29. Risk Management
In a nutshell, the process of identifying and assessing risks to decrease their negative impact on project operations is called risk management. During the process, it is made sure that overall project goals are not affected in any way.
30. Risk Mitigation
A strategy devised to decrease the probability of adverse effects of risk is known as risk mitigation. A successful risk mitigation strategy focuses on developing actions that reduce possible threats to overall project objectives.
31. Risk Monitoring and Control
Risk monitoring and control involve tracking how the risk responses are performing in comparison with the original risk management plan.
32. Risk Owner
A person responsible for ensuring that a particular risk is managed appropriately is a risk owner. One of the core duties of a risk owner is to make sure that the mitigation strategy is implemented effectively. He can also sometimes be involved with performing qualitative and quantitative risk analysis.
Issue Management and Bug Tracking Terms
33. Issue Management
The comprehensive process of identifying, resolving, and tracking issues associated with your projects comes under issue management. The purpose of issue management is to timely resolve the issues before they become big disasters.
34. Issue Tracking
Issue tracking is the process of identifying a possible bug or error in the product which is affecting its optimal performance. Most of the time, a professional issue tracking software is kept in place for efficient issue tracking.
35. Issue Log
A complete record of all the project issues (ongoing and closed), along with the persons responsible for resolving them is included in an issue log. The document may also include each issue’s status and resolution deadlines.
36. Issue Types
Issue type defines the particular category of an issue your project is likely to encounter during its lifecycle. The process makes assigning and tracking issues easy for their timely resolution.
Usually, there are three types of issues your project encounters over its lifetime:
- Bug – Any problem or issue that affects the functionality of your product
- Epic – A large chunk of work consisting of multiple issues is called an epic
- Story – Also known as ‘user stories’ are short feature requests from the perspective of an end-user
QA Project Management Terms
Quality of a project refers to a clearly defined set of deliverables by the stakeholders. What exactly do they want from a project is usually defined in terms of project quality. Common QA project management terms include:
37. Quality Planning
Quality planning identifies the expected quality standards that are to be met during the project, and creates systems which ensure these standards are met with effectiveness. In quality planning, it is determined how vigilant a team needs to be when fulfilling the quality standards.
38. Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance is a set of planned and systematic activities implemented to monitor the project processes in a way that project quality requirements are fulfilled. Quality assurance is done during the project and involves regular quality audits.
39. Quality Control
Quality control involves the use of standardized practices to evaluate whether the resulting product of a project meets quality expectations or not. The process is conducted after the product has been created to identify any changes that might be required in the quality assurance process.
40. Quality Management Plan
A quality management plan is a detailed plan consisting of stakeholders’ quality expectations, quality assurance, and quality control policies to successfully execute a project. This plan is usually a part of the project management plan.
This marks the end of our compilation of project management concepts. If you would like to make any corrections or additions to the list, please don’t hesitate to comment below.

